iv measurements to find oxide thickness|oxidation thickness chart : Brand Capacitance-Voltage (C-V) testing is widely used to determine a variety of semiconductor parameters, such as doping concentration and profiles, carrier lifetime, oxide thickness, .
webVer Fotos 83. Dados de interesse. No campo. Jardins, tenda. Cozinha para catering. Realiza apenas 1 evento por dia. Hospedagem disponível. Possui estacionamento. Ver .
{plog:ftitle_list}
87K Followers, 6,489 Following, 377 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Lindóya Parque - Alagoas (@lindoyaparque)
The measurement of electrical parameters from capacitance-voltage (C-V) and current-voltage (I-V) curves provides a fast means of characterizing oxides in MOS capacitors .Conduction Mechanisms. For relatively thick oxide layers, the IV response of “good” oxide is quite simple. At voltage biases well below break down, very little current flows (on the order of .
Oxide Thickness Measurement. The oxide thickness is an important parameter of the oxidation process, and thus many ways have been developed to measure it. Here we will describe few of the several methods for estimating .

In wafer processes, C-V measurements can reveal oxide thickness, oxide charges, contamination from mobile ions, and interface trap density.The goal of this work is to characterize MOS capacitance for gate oxides in the thickness range of 1.3–1.8 nm. In particular, modeling of the sharp decrease both in capacitance in the .
Capacitance-Voltage (C-V) testing is widely used to determine a variety of semiconductor parameters, such as doping concentration and profiles, carrier lifetime, oxide thickness, . A procedure based on energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy in a scanning electron microscope (SEM-EDXS) is proposed to measure ultra-thin oxide layer thicknesses .
ultra thin oxides pdf
Relatively thin oxide scale contributes to a reduction of boiler efficiency and causes persistent overheating of the tube wall. The growth of internal oxide scale is a time- .
Periodic measurement of scale thickness allows a plant operator to estimate remaining tube service life and to replace tubes that are approaching the failure point. Ultrasonic pulse/echo .layer with some spallation and (b) intact steam side oxide scale Determination of thickness of oxide layer has been used in recent years for the purpose of life assessment and failure analysis of components operating at high temperatures [2, 7]. Oxide scale thickness measurements permit the estimation of exposure time or temperature [10-11].
CV measurements as an analysis tool. 1) accumulation . depletion . 2) flat band . Lundstrom: 2018 . 3) inversion . 10 . CV measurements as an analysis tool • Oxide thickness • Flatband voltage • Doping density . Lundstrom: 2018 11 . More advanced techniques can also probe various types of charges in the oxide and at the
The calculations based on the mass center position of Si layer planes show that the average thickness of each layer is equal to 0.1296 nm, corresponding to the thickness of one-half oxide layer .
oxide thickness calculation
The current–voltage (I–V) characteristics of asymmetric (Al/Ta 2 O 5 /ITO) and symmetric (ITO/Ta 2 O 5 /ITO) RS devices are measured in current-perpendicular-to-plane geometry by changing the .
Three dimensional Not-And (3D NAND) flash memory devices are scaling in the vertical direction to more than 200 oxide/sacrificial wordline nitride layers to further increase storage capacity and enhance energy efficiency. The accurate measurement of the thicknesses of these layers is critical to controlling stress-induced wafer warping and pattern distortion. While traditional .This is where the oxide thickness can also be extracted from the oxide capacitance. However, for a very thin oxide, the slope of the C-V curve doesn't flatten in accumulation and the measured oxide capacitance differs from the actual oxide capacitance. . .Simple measurements of oxide charge using C-V measurements do not distinguish the three .
In wafer processes, C-V measurements can reveal oxide thickness, oxide charges, contamination from mobile ions, and interface trap density. These measurements continue to be important after other . The measurement of electrical parameters from capacitance-voltage (C-V) and current-voltage (I-V) curves provides a fast means of characterizing oxides in MOS capacitors or transistor structures. . In this work these effects have been incorporated into a rapid analysis program for extracting ultra-thin oxide parameters from measured C-V and I .
We use the approach to create top-gated 2D transistors with sub-0.5-nm-equivalent-oxide-thickness dielectrics that exhibit leakage current below the low-power limit of 0.015 A cm−2 at a gate .Decreasing the channel length and gate oxide thickness increases gm, i.e., the current drive of the transistor. Much of the scaling is therefore driven by decrease in L and tox. However if only these two parameters are scaled many problems are encountered, e.g., increased electric field.
TiO2 thin films of different thickness were prepared by the Electron Beam Evaporation (EBE) method on crystal silicon. A variable angle spectroscopic ellipsometer (VASE) was used to determine the optical constants and thickness of the investigated films in the spectral range from 300 to 800 nm at incident angles of 60°, 70°, and 75°, respectively. The . IV. MEASUREMENT OF OXIDE DEVELOPMENT WITH ANGLE RESOLVED X-RAY SPECTROSCOPY (ARXPS) ARXPS was used to measure the initial development of SiO 2 on Si . 19, and 33 days of exposure. We were unable to measure oxide thickness for exposure times longer than 33 days. Spectra from samples beyond 33 days were inconclusive, likely . Oxide thickness extracted from C – V measurement. Solid lines represent the extraction capacitance using the quantum-mechanical QM model. Circle markers represent the measured capacitance. The procedures for measuring the intensities and for subsequent calculation of the thickness of thermal SiO 2 layers on Si in the range 0.3–8 nm have been evaluated to determine the best measurement protocols. This work is based on earlier work where the measurements for (100) and (111) Si surfaces indicate the need to work at a reference .
oxide thickness
In this paper, results from C-AFM measurements using CoCr conductive coated probe tips are presented. Electrical oxide thickness of a range of oxides (Table 1) in the order of 1.6–5.04 nm thickness have been evaluated and compared with results using ellipsometry (optical thickness, d ox opt).For each tip/sample combination a statistical relevant number of . An international interlaboratory comparison on thickness measurements of graphene oxide flakes using atomic force microscopy has been completed in technical working area 41 of versailles project on advanced materials and standards. Twelve laboratories participated in the comparison project, led by NIM, China, to improve the equivalence of .
If t ox is the oxide thickness the C gb is given as : C gb = = Where ÃŽ ox is dielectric constant of the gate oxide, W is the drawn width and L drawn - 2L D is the effective channel length, L D is lateral diffusion length and L drawn is . Electrical oxide thickness of a range of oxides (Table 1) in the order of 1.6–5.04 nm thickness have been evaluated and compared with results using ellipsometry (optical thickness, d ox opt). For each tip/sample combination a statistical relevant number of IV-measurements were performed (Fig. 1). The thickness value has been obtained by .Portable ultrasonic instruments, such as the 39DL PLUS™ thickness gauge or the EPOCH™ series flaw detectors, can measure internal oxide layers down to a minimum thickness of approximately 0.2 mm or 0.008 in. using the commonly recommended M2017 transducer (20 MHz delay line). The specialized M2091 transducer, which is a 20 MHz shear wave .layer with some spallation and (b) intact steam side oxide scale Determination of thickness of oxide layer has been used in recent years for the purpose of life assessment and failure analysis of components operating at high temperatures [2, 7]. Oxide scale thickness measurements permit the estimation of exposure time or temperature [10-11].
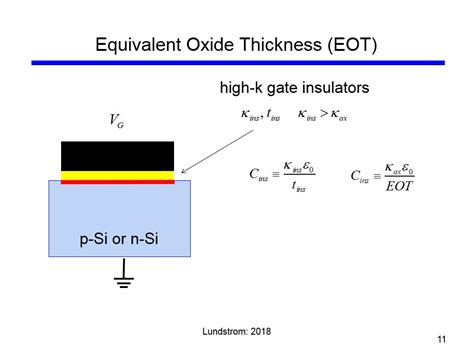
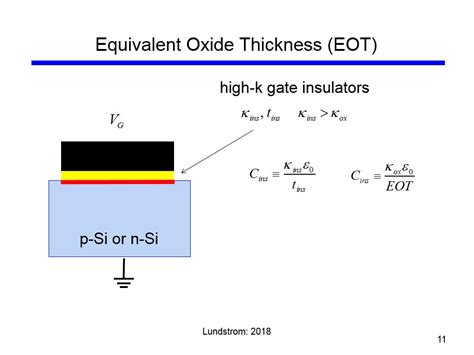
Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement of Internal Oxide Scale in Steam Boiler Tubes Steve LABRECK, Dan KASS, and Tom NELL IGAN, Olympus NDT, Waltham MA, USA . Typical internal oxide measurements with Pa nametrics-NDT Model 37DL PLUS thickness gage using 20 MHz transducer. Waveform on right has been zoomed to show details of oxide echo shape.The gate-oxide-channel structure forms acapacitor. The gate-oxide capacitance per unit area can be approximately calculated as: C ox = ε ox t ox (2.1) where ε ox = 0.351pF/cm is the permittivity (a dielectric constant) of SiO 2. Note that the capacitance is inversely proportional to the thickness of the silicon dioxide layer. Example Let the .ISO 2064, Metallic and other inorganic coatings — Definitions and conventions concerning the measurement of thickness 3 Term and definition For the purposes of this document the following term and definition apply. 3.1 local thickness the mean of the thickness measurements, of which a specified number is made within a reference areaAn equivalent oxide thickness usually given in nanometers (nm) is the thickness of silicon oxide film that provides the same electrical performance as that of a high-κ material being used.. The term is often used when describing field effect transistors, which rely on an electrically insulating pad of material between a gate and a doped semiconducting region.
one quantitative
The use of Dynamic Imaging Microellipsometry (DIM) for mapping and measuring oxide film thickness during growth has been demonstrated. The DIM system facilitates the analysis of oxide film characteristics by determining the polarization properties of a beam of light reflected from an oxide film/substrate system. For the extraction of the oxide-thickness from C-V measurements a new simple formula is suggested. The comparison of the different techniques shows very good agreement of the data within 2 Å for .
After that, a layer of oxide, approximately 500 Å thick, was grown on the Silicon wafers using a dry oxidation process at 650 C for 60 min, with a pre-ramp of 5 C per minute so that we reached at .
oq sample size
Chinese characters have been used in several different writing systems throughout history. The concept of a writing system includes the written symbols that are used, called graphemes—these may include characters, numerals, or punctuation—as well as the rules by which the graphemes are used to record language. Chinese characters are logographs, graphemes that denote words or
iv measurements to find oxide thickness|oxidation thickness chart